Bitumen Emulsion|Bitumen & Tar
0,00 €Bitumen Emulsions are Basically an O/W – Oil on Water Solution – A Dispersion of Bitumen Particles on Water, Stabilized with the Addition of Surfactants – Surface Active Agents – or Most Commonly known as Emulsifiers, that Will Permit the Bitumen to De Diluted in Water. They are Primarily Used for Tack Coats for use in Between Hot Mix Asphalt Lyers and Prime Coats for Thin Hot Mix Surfacing Layers or a Chip Seal Pavements.
Bitumen MC
0,00 €Liquid bitumen refers to bitumen that is the result of mixing bitumen with a lubricant (hydrocarbon or water). Ordinary and pure bitumens, such as 60-70 bitumens, are solid in ambient conditions and temperatures, and in order to use them, they must be heated to become liquid, but in many cases, it is not possible to use heat, or it is not economical, or heat. Causes decomposition of bitumen (burning bitumen) and it is not possible to use it cold. In these cases, liquid bitumen is used.
Bitumen VG
0,00 €According to zinc testers (or viscosity), it means: the penetration of a standard needle with a certain shape in millimeters under the effect of a load of 100 grams in 5 seconds in bitumen Which takes place at a temperature of 25 ° C. The obtained number indicates the permeability of bitumen
Butane Specification
0,00 €The product butane specifications are as follows:
| Capacity | 0.38 MTPA |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Butane Content | 95 liquid volume % (min.) |
| Pentane and heavier | 1.0 mole % (max.) |
| Quality | |
| Vapor pressure at 100 ºF | 70 psig (max.) |
| Volatile residue temp. at 95% evaporation | 36 ˚F (max.) |
| Corrosion, copper strip | No. 1 |
| Impurities | |
| Total sulfur | 0.001 wt % (max.) |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | negative |
Butane Specification
0,00 €The product butane specifications are as follows:
| Capacity | 0.38 MTPA |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Butane Content | 95 liquid volume % (min.) |
| Pentane and heavier | 1.0 mole % (max.) |
| Quality | |
| Vapor pressure at 100 ºF | 70 psig (max.) |
| Volatile residue temp. at 95% evaporation | 36 ˚F (max.) |
| Corrosion, copper strip | No. 1 |
| Impurities | |
| Total sulfur | 0.001 wt % (max.) |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | negative |
Butane-Hydrocarbons
0,00 €Butane or n-butane is an alkane with the formula C₄H₁₀. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. Butane is used as fuel and also as raw material in production of olefins.
Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve
0,00 €| Model : | Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve |
| Company name : | Iran Gas Valve |
| Packaging : | – |
| Minimum order : | 1 |
| Standard : | – |
| Production power : | – |
Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve Gas equipment
0,00 €| Model : | Butterfly |
| Company name : | Iran Gas Valve |
| Packaging : | – |
| Minimum order : | 1 |
| Standard : | – |
| Production power : | – |
Carbon dioxide Gas
0,00 €Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a nonflammable, colorless, odorless gas. It is found in air at concentration of about 0.03%. Carbon dioxide may exist simultaneously as a solid, liquid, and gas at a temperature of -56.6˚C and a pressure of 60.4 psig. At a temperature of -79˚C and atmospheric pressure, carbon dioxide solidifies forming “dry ice” at density of 97.4 pounds per cubic foot. Because of its low concentration in the atmosphere, air is not a suitable feedstock for carbon dioxide production. Rather, CO2 is obtained from by-product streams from various manufacturing processes. Bulk quantities of carbon dioxide are usually stored and shipped as liquid under elevated pressure and refrigeration.
Blanketing and purging of tanks and reactors. It is also used as shielding gas in the arc welding process. It is the source of the bubbles in soft drinks and other carbonated beverages. It is used to fill certain types of fire extinguishers that rely on its inert properties, densities, and low temperature when released from high-pressure storage.In addition to its “inert” properties, carbon dioxide, as dry ice, is used to freeze a variety of foods.
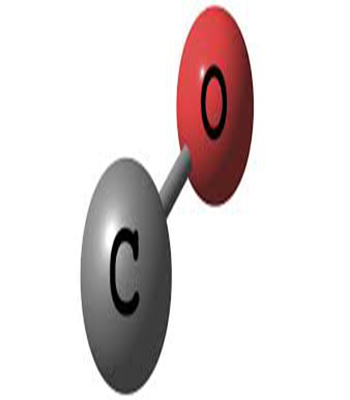
Carbon monoxide (CO) Gas
0,00 €Carbon monoxide (CO) gas is formed from the combination of a carbon atom with an oxygen atom. Not only flammable, it is also very hazardous since it is very toxic and odorless. It cannot sustain life and is produced, among other things, from incomplete combustion due to lack of oxygen. It can therefore cause domestic accidents if heating systems are poorly maintained. It is produced on a large scale in industry, in combination with hydrogen, by reforming hydrocarbons, generally natural gas. It is used in large quantities to produce various intermediary organic chemicals, such as acetic acids, isocyanates, formic acid, and also certain polymers such as polycarbonates and polyketones.
Carbon Monoxide Gas
0,00 €The Co unit production capacity is 140 kt/y of Carbon Monoxide,the feed of which is natural gas received from the National Iranian Gas Company at the rate of 87927 T/Y. The feed is mixed with steam after desulphurization and flow through the pre reformer at which higher hydrocarbons are broken to methane,CO,CO2 and Hydrogen and then passes through the reformer where sysngas is formed from the endothermic reaction of methane with steam .The reformer outlet steam is cooled to condensate and separate water ,then its CO2 content is separated by amine solution and returned to the reformer and discharged H2&CO are separated in a cold box to produce pure carbon monoxide product.